INTRODUCTION¶
Background to RRAMS¶
The Rural Roads Asset Management System (RRAMS) grant has been established to ensure efficient and effective investment in rural municipal roads, through the development of a Road Asset Management Systems (RAMS). The grant is provided by National Treasury and administered by the National Department of Transport. The aim is to capacitate district municipalities to set up rural a RAMS and collect road and traffic data on municipal road networks, in line with the Road Infrastructure Strategic Framework for South Africa (RISFSA)
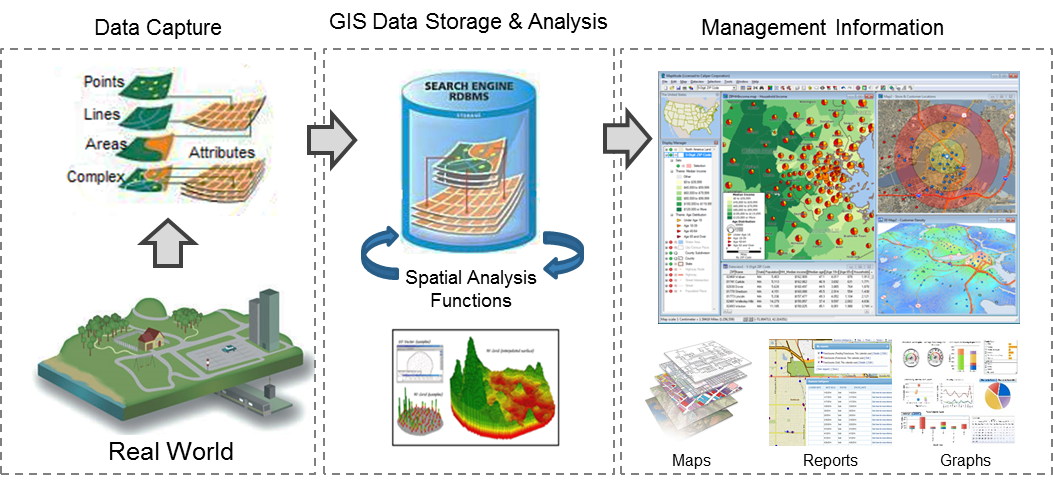
GeoRAMS is a web based enterprise GIS platform, that was specifically developed to store, process, analyse and present RRAMS data. This document is a guideline for users of GeoRAMS and explains the different features and functions of the platform.
What is GIS?¶
A geographic information system (GIS) is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyse, manage, and present spatial or geographic data.
GIS applications are tools that allow users to create interactive queries (user-created searches), analyse spatial information, edit data in maps, and present the results of all these operations.
GIS Terminology¶
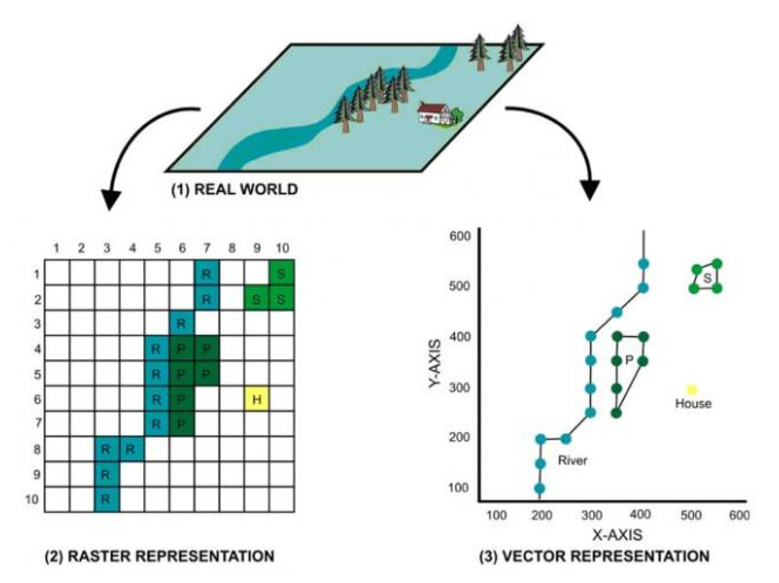
- Raster data: raster data is made up of pixels where each pixel value corresponds to a specific colour. The data is represented in a grid of cells (usually square). Putting these grids together allows the GIS to build a map. Examples of raster data is satellite images or aerial photographs
- Vector data: vector data consists of individual points that can be joined together to form lines and polygons
Example of raster representation |
Example of vector representation |
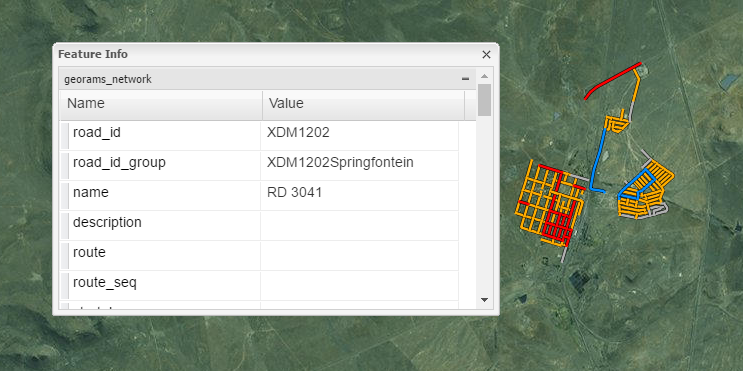
- Attribute data: attribute data is information appended in tabular format to spatial features that describes the spatial data. Spatial data represents the “where” and attribute data can contain information about the “what”, “where” and “why”.
- Feature: a feature is a representation of a real-world object on a map, such as a town or a road. It is a point, line or polygon object that can be used in a GIS for storage, visualization and analysis.
- Layer: a layer is a group of features of the same type, for example, a district boundary will have a number of line features demarcating different districts)
- Map: a map is an interactive presentation of different layers that is aimed at communicating a specific theme, for example, a map of all the roads in a specific municipality